Introduction: Shaping the Future with Sustainable Industrial Design
In recent years, sustainable industrial design has shifted from a niche concept to a crucial focus for companies and designers worldwide. As awareness of climate change and environmental degradation grows, industries are under increasing pressure to adopt eco-friendly practices that minimize waste, reduce carbon footprints, and conserve natural resources. Sustainable design is no longer just a choice; it’s becoming an essential aspect of responsible manufacturing and product development.
This article explores how sustainable practices are shaping the future of industrial design, focusing on innovative materials, renewable energy sources, and waste reduction strategies. By integrating sustainable materials, designing for durability, and harnessing renewable energy in production processes, companies can meet the demands of a rapidly changing market and align with consumer expectations for environmentally responsible products.
From reducing waste to embracing circular economy principles, sustainable industrial design holds the potential to transform how products are created, used, and disposed of. In the following sections, we’ll delve into practical strategies, challenges, and opportunities that come with adopting sustainable practices, examining how they can drive growth, reduce environmental impact, and shape a greener future for the industry.
Using Sustainable Materials and Recycling in Industrial Design
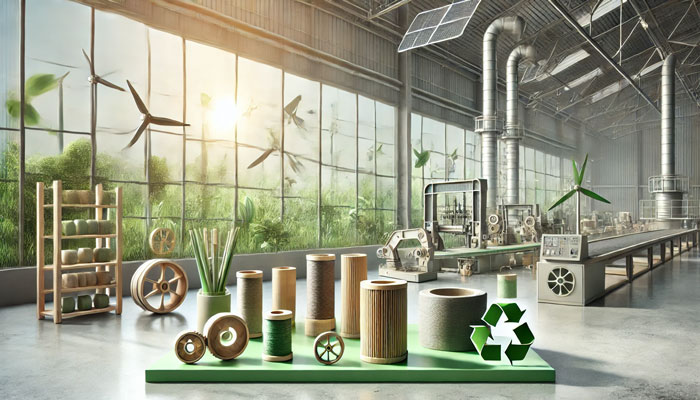
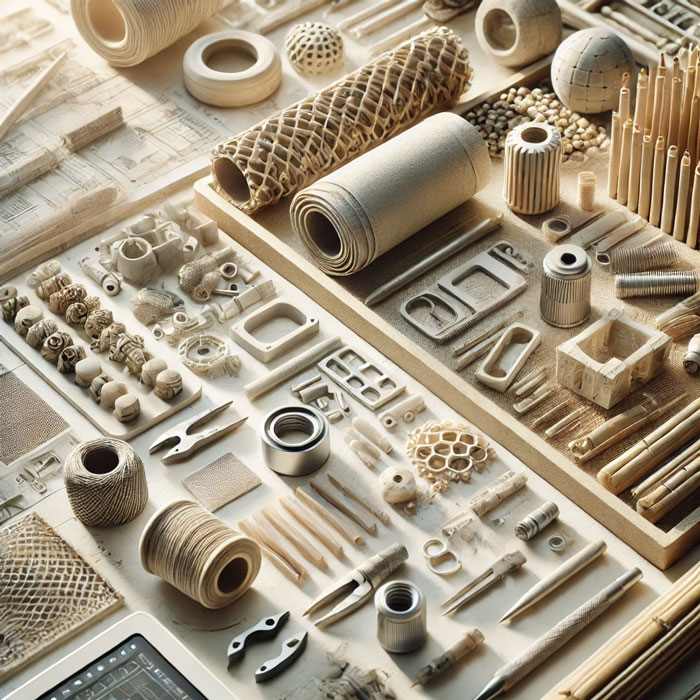
A critical component of sustainable industrial design is the use of eco-friendly materials that minimize environmental impact throughout a product’s lifecycle. From recycled plastics and biodegradable materials to innovative plant-based substances, designers today have more options than ever to create sustainable products. Choosing materials that can be easily repurposed or decomposed reduces waste and energy consumption, supporting the shift towards a circular economy.
Recycled materials, such as post-consumer plastics and metals, are widely utilized in sustainable design, offering durability while reducing reliance on new raw materials. Some companies even repurpose waste materials from other industries, transforming them into new, valuable products. Biodegradable materials like bamboo, mycelium, and certain bioplastics also offer alternatives that break down naturally over time, preventing long-term pollution.
By incorporating these sustainable materials, designers contribute to a more eco-friendly manufacturing process and promote resource efficiency. As technology and innovation continue to advance, sustainable material options will expand, empowering designers to create products that are as responsible as they are functional.
Designing for Durability and Minimizing Waste in Industrial Design
A cornerstone of sustainable industrial design is the focus on creating products with longevity and minimal waste generation. When products are designed for durability, they are more likely to withstand prolonged use, reducing the frequency of replacements and the demand for raw materials. This approach not only benefits the environment by lowering overall waste but also appeals to consumers who value quality and reliability.
One effective strategy is designing modular products with replaceable parts, allowing for easy repairs or upgrades rather than complete replacements. This extends the product’s life cycle and reduces waste from discarded items. Additionally, minimalist design principles help designers avoid unnecessary materials and features, optimizing efficiency without sacrificing function.
By designing for durability and reducing waste, industrial designers can play a pivotal role in promoting sustainable consumption and production. These practices also support circular economy goals, where products and materials are kept in use as long as possible, ultimately reducing their environmental footprint.

Integrating Renewable Energy into the Production Process
In the journey toward sustainable industrial design, utilizing renewable energy sources in manufacturing is a vital step. Shifting away from fossil fuels and adopting renewable energy solutions like solar, wind, and hydropower can significantly reduce a company’s carbon footprint. This not only contributes to a cleaner environment but also aligns with global sustainability targets and consumer demand for greener production methods.
Renewable energy can be integrated at various stages of the production process. For instance, solar panels can power manufacturing plants, while wind turbines can generate electricity for factories in suitable locations. Some companies are even exploring bio—energy derived from organic materials—as a sustainable fuel alternative. Additionally, energy-efficient practices, such as waste heat recovery systems, further reduce the reliance on traditional energy sources.
Adopting renewable energy not only enhances sustainability but also builds brand value as companies demonstrate their commitment to eco-friendly practices. With advances in technology making renewable energy more accessible and cost-effective, the integration of sustainable energy solutions in industrial design is becoming a practical choice that can shape a greener future for the industry.
Challenges and Opportunities in Adopting Sustainable Industrial Design
While sustainable industrial design offers numerous benefits, transitioning to eco-friendly practices comes with its own set of challenges and opportunities. Adopting sustainable materials, implementing renewable energy sources, and designing for durability require substantial investments, research, and often a complete shift in production processes. For many companies, this transformation can be costly and time-consuming, presenting significant operational hurdles.
However, these challenges are also opportunities for innovation and leadership within the industry. Companies that overcome these obstacles can differentiate themselves in a competitive market, attracting eco-conscious consumers and building long-term brand loyalty. Moreover, advancements in technology and global support for sustainability efforts continue to make sustainable design more accessible and affordable.
By navigating the complexities of sustainable industrial design, companies can position themselves as pioneers in environmental responsibility, gaining a competitive edge and contributing to a healthier planet. This balancing act between challenges and opportunities highlights the importance of strategic planning and commitment to sustainability as the industry moves toward a more sustainable future.
Conclusion: Paving the Way to a Sustainable Future through Industrial Design
The shift toward sustainable industrial design is more than just a trend; it’s an essential evolution in response to the urgent environmental challenges facing our world. By adopting sustainable materials, designing for durability, incorporating renewable energy, and overcoming implementation challenges, industrial designers have the power to drive meaningful change and reduce the ecological impact of the products we use every day.
The journey toward sustainability may come with its complexities, but the benefits—environmental, economic, and social—are profound. Companies that embrace these practices not only contribute to global sustainability goals but also meet the growing demand from consumers for responsible products. As technology continues to advance, opportunities for sustainable innovation will expand, paving the way for new solutions that align with eco-friendly values.
Ultimately, sustainable industrial design isn’t just about creating products that perform well today; it’s about designing for a future that prioritizes the well-being of our planet and its resources. By building a foundation of responsibility, resilience, and innovation, the industrial design industry can lead by example, demonstrating that sustainable choices are both achievable and essential for a healthier, more sustainable world.